How To Improve Google Page Experience For Better Ranking In 2022
If you want to improve Google page experience, you got to know what it is all about. In essence, Google is trying to tell you as a user or as a webmaster that you need to put the user first. If you put the user first and strive hard to provide them with the best user experience, Google will rank you higher in the long run as it benefits a user which pleases Google. And if the users are happy while using Google’s search engine, what will they do? They will keep coming back and Google more, which helps Google generate more revenue.
Table of contents:
-
- What is Google Page Experience and Why does it matter?
- What are Web Vitals?
- How do Core Web Vitals affect the Website?
- Why Google Page Experience is Important?
- Tips to Improve Google Page Experience
Google follows the trend. Remember that it doesn’t care about you or your website; today, it has become more user-centric. So, you need to focus on both – SEO (Search engine optimization) and UX (user experience) to give your readers the best possible experience and thereby increase your page ratings and site’s performance.
So, first off let us understand Google’s latest algorithm update – “Google Page Experience”.
What is Google Page Experience and Why does it matter?

Google Page experience is Google’s latest attempt to improve search engines for users. Page experience update started rolling out on 15th June and it is Google’s new input for search ranking. It is a set of signals that calculate how users perceive the experience of interacting with a web page on the computer and mobile devices. Google’s new algorithm update combines the core web vitals and previous user-experience-related search signals to measure the Google page experience.
What goes into Page Experience?
There are a few core page experience signals, that Google has identified as a part of this new update:
1. Boolean checks
-
- Mobile-friendliness
- Using HTTPS
- No intrusive interstitials
- Safe browsing
2. Core web vitals
-
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
All of these factors allow you to identify the issues that hinder online readers from accessing a wealth of valuable information on the web. Google’s focus on these Google page experience metrics aligns with recent search marketing trends that have moved beyond traditional On-page SEO strategies such as keyword density, page metadata, etc.
The advance technical SEO strategy prioritizes the improvements of a website’s user experience through code-level enhancement. User experience plays a vital role in the ranking law of search, and the Google page experience update has provided you with a roadmap to follow.
What are Web Vitals?
Web vitals is an initiative taken by Google to provide unified guidance for quality signals that are essential to serve a better user experience.
Core web vitals are the subset of web vitals that apply to all pages. Core web vitals are the metrics that help webmasters, marketers, or site owners to keep track of their web pages and optimize the website to deliver a great user experience. These web core vitals measure the ability of a website to offer users a better browsing experience with optimal speed, visual stability, and responsiveness across computers and mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. The metrics that makeup web vitals will evolve over time.
How do Core Web Vitals affect the website?
Here are a few factors that affect the core web vitals and thereby hurt your page experience:
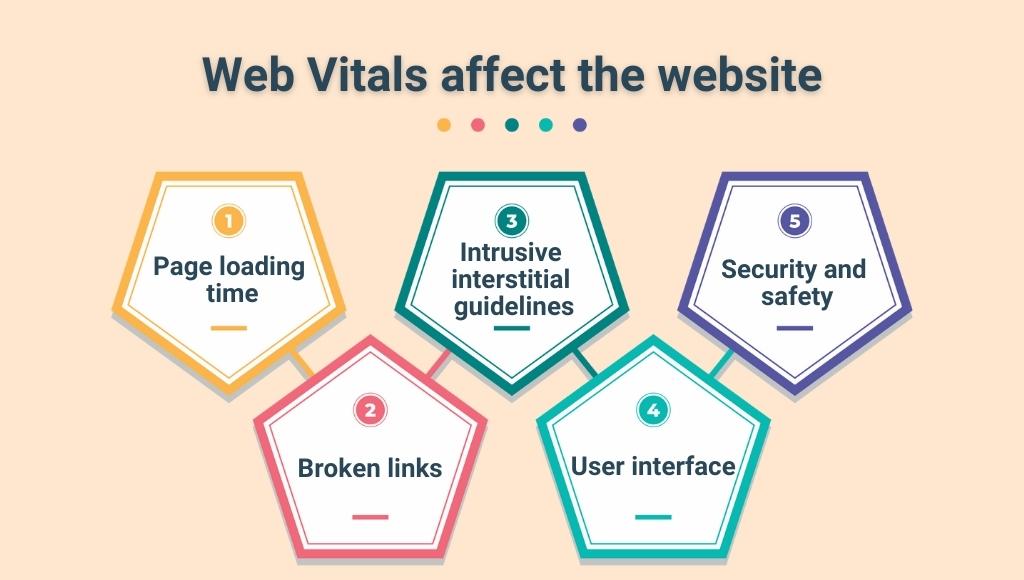
- Page loading time: If your site takes a lot of time for loading a page, your users will likely leave that page right away. You need to increase your page speed to provide a better user experience.
- Broken links: Links that fail to land on a page, or return a 404-error message are called “broken links” or “link rots”. Having such dead links on your page may damage your website’s ranking.
- Intrusive interstitial guidelines: Intrusive popups block a user from having smooth access to your web page. Showing popups that cover the main content of the page makes the content less accessible to the users. And it is really annoying!
- User interface: It is very important to have a mobile-friendly website as Google likes a mobile site. If your website is unresponsive, neglects security, and is not optimized for SEO then staying indifferent to the trends may earn you a rebel title as the “Bad website design”. You need to focus on web designing and web development to improve your site’s performance on computers as well as mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
- Security and safety: Google, promotes internet safety and security. Safe browsing is Google’s first priority. Having a website that is labeled as “not secure” by Google chrome will harm the trustworthiness of the website. That is why an SSL certificate is important. It helps to reduce the fraud rate and protect user privacy.
Core web vitals consist of three metrics that measure the overall page experience of a website.
1. Largest contentful paint (LCP)
LCP is the first metric of the web core vitals. It indicates how long it takes for the largest content of the page to load. The length of time taken by the largest content to load is called the “Largest contentful paint”. LCP that takes 2.5 to load the effective content is considered good. If your site takes more than 4 seconds then you are in trouble.

For example, suppose that you are browsing a new website and opened a new article to read, LCP for that page would occur when the main featured image of the article was loaded because images are heavier than texts. Lightweight page elements and the texts are typically loaded first.
2. First input delay (FID)
FID measures the time taken by the site to respond to the user’s input such as clicking, and tapping a button or a link. Google wants every website to be interactive and responsive as fast as possible once they are opened by the users. For example, if you clicked an interactive element such as a Call-to-action button, the time taken by the computer to register your click and respond is FID.
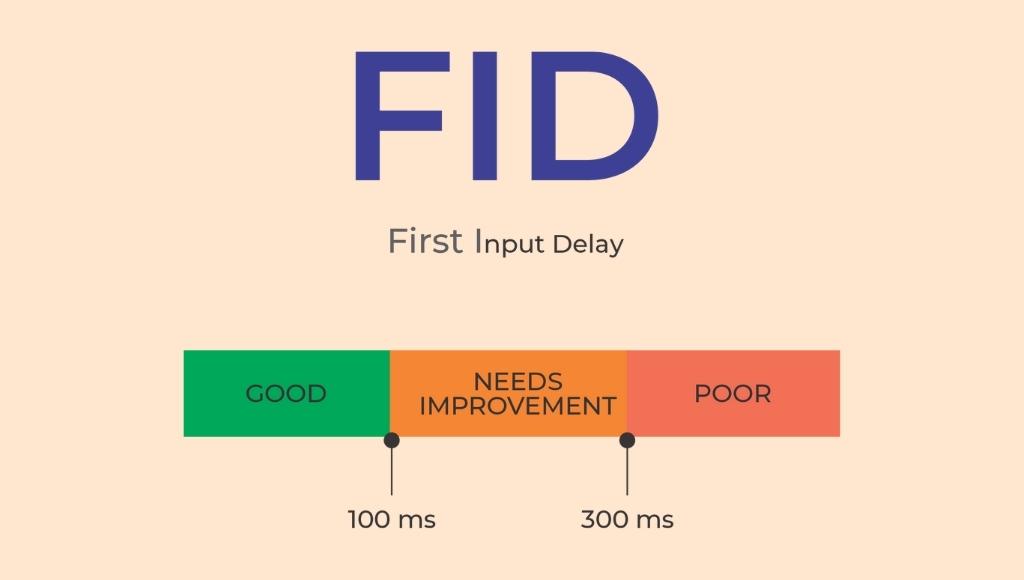
Generally, the response time should be less than 100ms, that’s a tenth of a second. Just like a blink of an eye. Google wants – the moment a user is ready to act, the website needs to be ready to respond. A score under 100ms is considered good or passing.
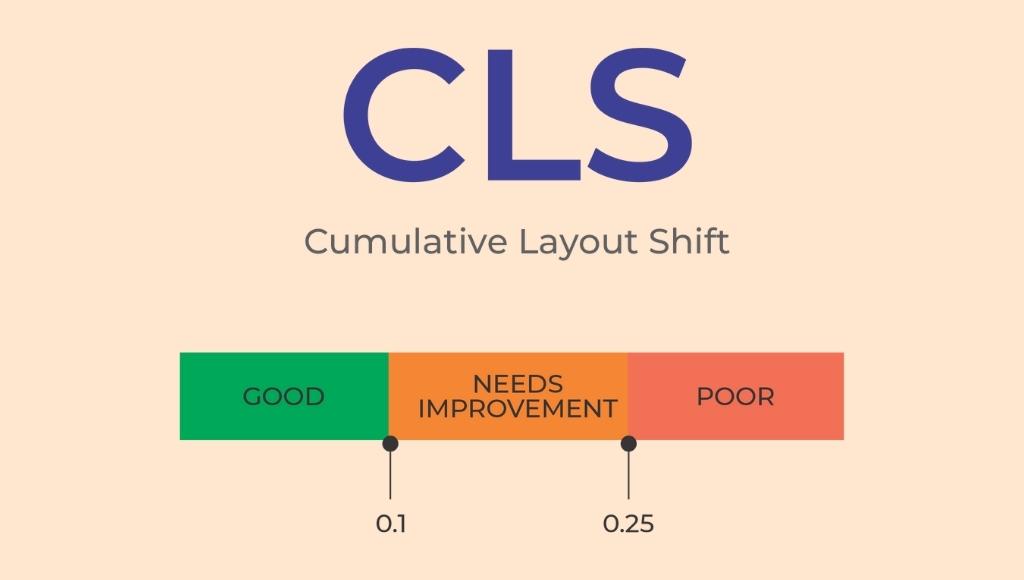
3. Cumulative layout shift (CLS)
CLS is the last metric in the web core vitals. It accesses the stability of a page. For example, if someone is trying to read content and the page moved, so you have to find your place in the article once again, or if you are trying to tap a button and the page moves unexpectedly and you are forced to click the wrong button, then you have been a victim of a bad CLS. That’s a page layout shift which is called a “cumulative layout shift”. CLS is the total change in the layout of a web page as it loads. A score under 0.1 is considered good or passing.
According to Google research, having a poor core web vital score and page experience:
- Reduces the conversion rate: There is a strong relationship between conversions and a good page experience. Pages that load in 2.4 seconds have a better conversion rate.
- Increases the bounce rate: Longer page loading time has a major impact on the bounce rate.
- Generate less revenue: Speedy rendering times generate more revenue than the average and vice-versa.
Websites that have a bad user experience find it difficult to rank higher on Google and drive traffic from SERPs. Optimizing a website with the latest update along with SEO has become one crucial part of marketing strategies.
Tips to Improve Google Page Experience
If you want your website to be rewarded, rather than penalized, with the rollout of the latest Google update “page experience”, here are a few tips to improve your Google Page experience to provide the best possible UX.
1. Use a responsive web design
If you are not using a responsive web design, then now is the time to upgrade your website.
2. Upgrade to HTTPS
Google wants to provide its users with a secure and safe browsing environment. Getting an SSL certificate through your domain registrar is inexpensive and easy. HTTPS protocol has been added as a page experience signal by Google in its new rollout update, so if you want to achieve a “good page experience” status in Google search results then, a page must have an HTTPS encryption.
3. Increase the security of your website
Work hard to achieve better standards for user privacy, fraud reduction, and overall safety.
4. Remove popups
Remove annoying elements or intrusive interstitial guidelines that block the access of the users.
5. Cleanup backend code
Several improvements can be done to the backend code to improve page loading time and provide a better user experience. You can remove the unused JavaScript, utilize modern file formats, and minimize large JF libraries with local CSS and JavaScript libraries for building user interfaces.
6. Use a good caching plugin
A good caching plugin can help you store your website’s information so it loads much faster than before for repeat visitors.
Conclusion
Google page experience update is going to evolve significantly along the way. With this initial rollout, Google wants to reward the sites that offer a high-quality user experience while de-ranking sites that provide a poor user experience. So, optimizing your website for this latest Google update should be your highest priority.
Do you need help in improving your website’s page experience?
We have the best search marketing experts who specialize in both web development and search engine optimization.
Connect with us to set up a free consultation.